Basal Cell Carcinoma - Symptoms & Causes
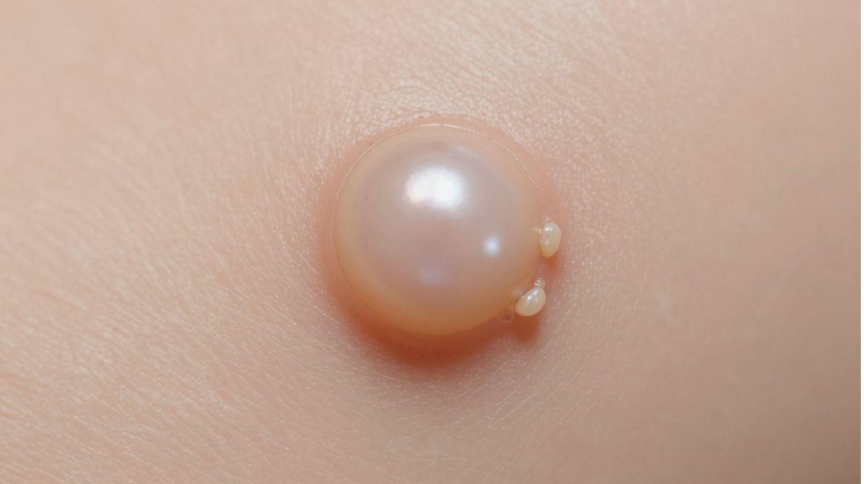
Basal cell carcinoma, often called BCC, is the most common type of skin cancer. It starts in the basal cells, which are found at the bottom of the outer layer of your skin. These cells help make new skin cells. While BCC usually grows slowly and doesn't often spread, it's still important to know about its signs and causes. Many cases are linked to sun exposure, but other factors can play a role too.
Key Takeaways
- Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common skin cancer and usually grows slowly.
- Long-term exposure to UV radiation from the sun or tanning beds is the main cause.
- Common signs include shiny bumps, flat scar-like areas, red patches, or sores that don’t heal.
- Family history, genetics, and a weak immune system can increase risk.
- Sun protection helps reduce the risk of BCC.
What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma?
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) begins in the basal cells of the epidermis, the skin’s outermost layer. These cells create new skin cells as old ones die off. BCC often appears on sun-exposed areas like the face and neck and usually grows slowly.
- Shiny or pearly bump
- Red or irritated patch
- Sore that doesn’t heal
- Waxy or scar-like area
Why Basal Cell Carcinoma Develops
BCC develops mainly due to DNA damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. Over time, repeated exposure can cause abnormal cell growth.
- Chronic sun exposure
- Tanning bed use
- Fair skin type
- Weakened immune system
- Previous skin cancer
- Radiation therapy
Common Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
BCC often appears on sun-exposed areas such as the face, ears, neck, and scalp. It may develop slowly and look different from person to person.
- Shiny, pearly bump
- Flat scar-like spot
- Open sore that doesn’t heal
- Pink growth with raised edges
- Red, itchy patch
Treatment Considerations and Patient Benefits
Treatment depends on the size, depth, and location of the cancer. Most cases are highly treatable, especially when detected early.
- Surgical removal
- Topical treatments
- Radiation therapy
- Targeted or immune therapies
Reducing the Risk of Future Skin Cancer
Protecting the skin from UV exposure is the most effective way to lower the risk of future skin cancers.
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen
- Wear protective clothing
- Avoid tanning beds
- Check skin regularly
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is basal cell carcinoma?
- What causes basal cell carcinoma?
- What are common symptoms?
- Who is at higher risk?
- Can it be prevented?
- When should a doctor be consulted?


